Laser Speckle Contrast Imaging (LSCI) has emerged as a vital tool in stroke research, providing researchers with the ability to assess cerebral blood flow dynamics non-invasively. This innovative technology enhances the understanding of ischemic events and offers insights into potential therapeutic interventions for stroke patients.
Mechanism of LSCI Technology
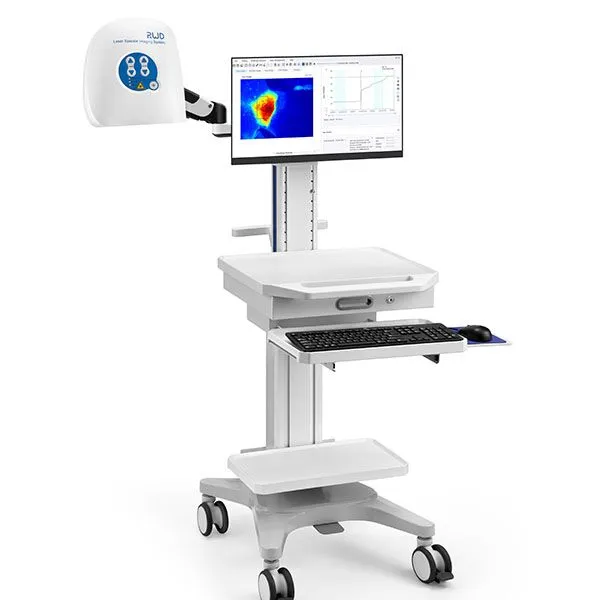
The laser speckle contrast imaging LSCI technique employs coherent light to illuminate tissues, capturing the scattering patterns created by moving blood cells. This non-contact method does not require the use of contrast agents, which eliminates potential complications and risks. The RFLSI ZW model from BPLabline exemplifies the advanced capabilities of modern LSCI systems, offering high spatial resolution and frame rates up to 100 frames per second.
One of the major benefits of using LSCI in stroke research is its ability to visualize blood flow in real-time. Researchers can monitor blood perfusion changes in various tissues, including the brain, by examining the speckle patterns obtained from tissue surfaces. This allows for precise measurements of cerebral blood flow and can help establish critical correlations between blood flow restoration and recovery outcomes in stroke models.
Additionally, the laser speckle contrast imaging system provides quantitative data on blood perfusion, making it valuable for studying conditions like middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). This model closely simulates the effects of ischemia, and LSCI enables researchers to assess the impact of therapeutic interventions over time.
Applications of LSCI in Stroke Research
In the context of stroke research, the applications of laser speckle contrast imaging LSCI are extensive. It allows for continuous monitoring of cerebral blood flow during acute ischemic events and the assessment of recovery techniques. Understanding how blood flow dynamics change in response to various therapeutic strategies is essential for developing effective treatments for stroke patients.
Furthermore, LSCI facilitates the study of mechanisms like cortical spreading depression, a phenomenon that can exacerbate damage following an ischemic stroke. By analyzing blood flow responses during these events, researchers can gain valuable insights into secondary injury processes that can affect patient outcomes.
The versatility of the laser speckle contrast imaging system also extends to other applications in vascular research. It has proven useful in studies involving hind-limb ischemia and assessing organ microcirculation. With adoption across numerous respected institutions, including Stanford University and Yale University, LSCI has been instrumental in supporting the publication of numerous research papers, thereby enhancing scientific knowledge in the field.
Paving the Way for Stroke Intervention Research
In summary, LSCI has revolutionized stroke research by offering a non-invasive and effective means to measure cerebral blood flow. The ability to visualize and quantify hemodynamic changes in real-time using laser speckle contrast imaging LSCI is crucial for advancing understanding in this critical area of medicine.
As technologies like the laser speckle contrast imaging system continue to evolve, they promise to enhance research efforts aimed at tackling stroke and improving recovery outcomes. The insights gained from employing LSCI will undoubtedly drive innovations in treatment strategies, ultimately benefiting patients and advancing clinical practices in stroke management.